How GST Benefits Us? Advantages and Disadvantage of GST Taxation System
- January 14, 2020
- Posted by: Editorial Team
- Category:
In the year 2017, the government of India passed a bill, which is called the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Act. This new taxation system was formed to supersede the Value Added Tax (VAT) for all goods and services, both within the country and at international level (exports and imports). This new tax regulation was enforced to also prevent taxpayers who evade paying their taxes, whether they file their taxes monthly, quarterly or annually.
Therefore, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) can be defined as an indirect taxation system that is imposed on all types of goods supplied to consumers and businesses, as well as services that are rendered to individuals and/or businesses within and outside the country.
In this article, we are going to take a look at the various advantages as well as some of the disadvantages pertaining to the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Act, 2017.
Advantages of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Taxation System
Given below are some of the major advantages of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and how this indirect taxation system benefits us as consumers and taxpayers.
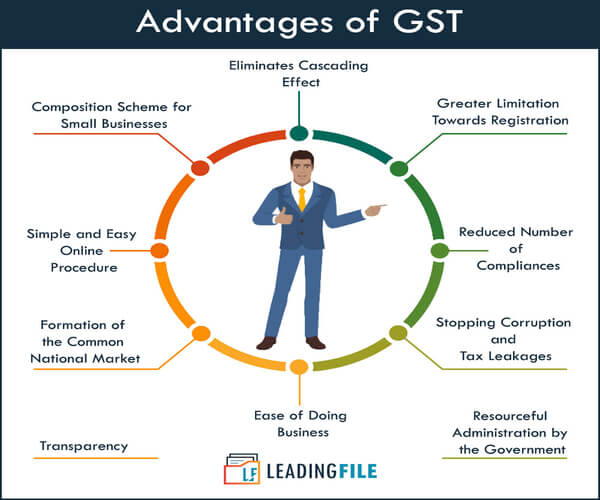
Pros of GST (Goods and Services Tax)
(a) Eliminates Cascading Effect
The primary purpose of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Act, 2017 is to bring the indirect taxation system under one roof and that would further eliminate the cascading effect of the tax. This cascading tax effect is also better known as ‘taxation over previous tax’.
Example:
Here, we are going to make a brief comparison of the taxation system both before and after the formation of GST.
Scenario prior to GST taxation system
Let’s consider an example here, where a person offers consultation services for a fee of Rs. 50,000 and is imposed 15 percent of service tax. So, if we calculate the service tax of 15 percent for the service the person is rendering to his/her clients at a cost of Rs. 50,000, then he/she pays tax amount of:
Rs. 50,000.00 x 15/100 = Rs. 7,500.00
Furthermore, if the person wishes to purchase supplies for his/her office, say, costing Rs. 20,000.00 for which he/she pays VAT (Value Added Tax) of 5 percent on the purchase, the taxed amount is:
Rs. 20,000.00 x 5/100 = Rs. 1,000.00
Therefore, from the above equation, it is seen that the person paid service tax of Rs. 7,500.00 and an additional tax for the supplies, which makes a total of Rs. 8,500.00. This sum is the net tax that the person pays under the traditional taxation system prior to the introduction of the revised GST.
The scenario under GST taxation system
Now, let’s take a quick look at the current GST taxation system. Here, taking the same example as stated above, the person is only liable to pay GST tax of 18 percent off Rs. 50,000, which is for rendering services to his/her clients.
Rs. 50,000.00 x 18/100 = Rs. 9,000.00
The amount of Rs. 20,000.00 paid towards purchasing office supplies along with 5 percent tax is, therefore, relaxed.
Rs. 20,000.00 x 5/100 = Rs. 1,000.00
So, the person’s net GST payable now is Rs. 8,000.00, which is only a fraction less than what he/she paid in the earlier taxation system.
(b) Greater Limitation towards Registration
Previously, under the VAT taxation system, a person or business making a turnover of over Rs. 5,00,000 in certain states, was levied a VAT. This differed from one state to another state. Also, a person or business rendering services to his/her clients were exempted from paying service tax, if their annual turnover was up to Rs. 10,00,000.
However, under the GST regulation, this limitation was increased to Rs. 20,00,000 for the rest of the states and Rs. 10,00,000 for hill states, where small traders and service providers were exempted from paying service tax. This limitation is enforced in the state of Himachal Pradesh and few states in the north-eastern region, such as Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Sikkim, and Tripura.
(c) Composition Scheme for Small Businesses
Small businesses having a turnover of more than Rs. 20,00,000 and up to Rs. 75,00,000 may benefit because, under GST, this creates an opportunity to reduce tax by utilizing the composition scheme. This move has eliminated the burden of compliance and tax for several small-scale businesses.
(d) Simple and Easy Online Procedure
GST is said to make the taxation system a much efficient procedure for taxpayers. Right from the process of registration to filing one’s returns (whether monthly, quarterly or annually) is made available online. Because of the rapid improvements in technology, individuals and businesses, including start-ups, can greatly benefit from this as it will not be required to physically visit every department to apply for separate registrations, like VAT, excise and service tax. All of this can easily be done online. There is an official government portal, where you will find various services related to GST.
(e) Reduced Number of Compliances
Previously, there used to several compliances and returns filing, such as excise, VAT and service tax for the respective goods and services that were carried out by individuals and businesses. Now, under the new GST regulations, things have changed to the betterment of taxpayers. There are a unified return filing and the number of returns to be filed has been greatly reduced to just one.
In total, there are about 11 returns under the GST, which are further divided into four basic returns that apply to all taxable persons under GST. The main is GSTR-1, which is filled manually by taxpayers, while GSTR-2 and GSTR-3 are filled automatically.
(f) Stopping Corruption and Tax Leakages
The taxpayer can directly register on India GST government portal/website, file returns and make payments of the taxes without having to associate with any tax authorities. A network has been set to match the invoices of the supplier and buyer. It monitors tax fraud and evasion and brings more businesses into the formal economy.
(g) Formation of the Common National Market
GST has boosted India’s tax GDP(Gross Domestic Product) ratio which helps in promoting economic efficiency and long term growth. This led to uniform tax legislation between different sectors related to indirect taxes. It helps to overcome economic distortion and creates a common national market.
(h) Ease of Doing Business
The problems in indirect tax compliance have been decreased due to the implementation of GST. Previously companies had to face several problems related to registration of VAT, excise customs, working with tax authorities, etc. The benefit of GST has helped companies to run their businesses easily.
(i) Transparency
The structure of previous GST indirect taxes prevents transparency. GST is a general tax system. This will produce the necessary information to the end customer, which creates a transparent environment.
(j) Resourceful Administration by the Government
The old tax system was a complicated task to management for the government. However, under the GST establishment, the information such as the integrated tax rate, merged GST network, simple input of the tax credit mechanism are available and the administration of resources is well-ordered and clear for the government.
Disadvantages of Goods and Services Tax (GST) Taxation System
In contrast to the major advantages of Goods and Services Tax (GST) and their benefits to taxpayers, we shall also take a quick look at some of the disadvantages of this indirect taxation system and how it impacts businesses and individual taxpayers.
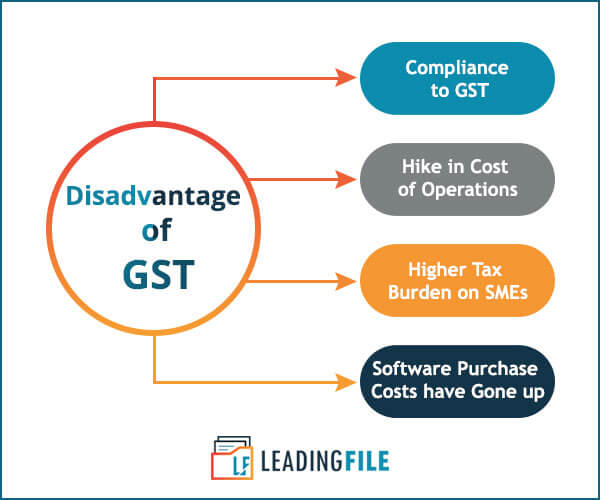
Cons of GST (Goods and Services Tax)
(a) Compliance to GST
The GST Act, 2017 enforces various regulations that are mandated to both individuals and small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Thus, SMEs that have not registered for GST before, will have to learn the nuances of this taxation system at a quick rate. Upon signing up or registration, individuals and businesses will be permitted access to various services like issuing invoices that comply with GST, adhering to digital record-keeping, timely filing of returns and much more.
The invoice that is allotted in compliance with the GST is needed to contain essential information like the taxpayer’s Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN), product’s HSN code, place of supply and so on.
(b) Hike in Cost of Operations
Many businesses will be compelled to employ tax professionals who are more compliant with the new GST regulations. However, this may also cause a gradual hike in the cost of operations for small businesses, since they will have to bear the burden of spending more money as the cost of hiring experts. Also, many businesses will have to spend extra money on the training of their employees under the compliance of GST, thereby increasing their overall expenditure.
(c) Higher Tax Burden on SMEs
Under the new GST regulations, there may be challenges experienced by many small businesses, especially the ones in the manufacturing sector. Now, such businesses that make a turnover of over Rs. 20,00,000 annually will be liable to pay GST. Previously, businesses that made a turnover of more than Rs. 1,50,00,000 were mandated to pay excise duty.
In the case of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) having a turnover of Rs. 75,00,000 may choose the composition scheme and only pay a 1 percent tax on the turnover in lieu of GST and benefit from the lesser compliances. However, such businesses will not be able to claim any input tax credit. Thus, this may further make it even more difficult for businesses to decide whether to choose the composition scheme or increased taxes.
D) Software Purchase Costs Have Gone Up
Businesses buy ERP software or update their existing accounting systems to comply with GST and file accurate returns on time. These options have increased the cost, allow the software to buy and training employees to use the new billing software application most efficiently.
E) Online Procedure
GST is an online taxation system, due to which many businesses or business owners face difficulty in paying taxes. Most businesses use manual filing procedures. Online Processes may cause an issue in compline and confusion. So, It might become difficult to use the online system and adjust to it.
Bottom Line
Although the Goods and Services Tax (GST) taxation system may pave a new path for both individuals and businesses of any size, this may also help reduce the many challenges that might be experienced by taxpayers at a later point in time.
